- From Digital Transformation to Hyper-automation
- How Flow can affect your productivity and work
- RPA is not AI; Combine them for Superpowers
- Hyper-automation is the Pinnacle of Digital Strategy
Automation is becoming the go-to term in several industries. From self-driving cars to social media posts, automation has become omnipresent. According to a report, Robotic process automation (RPA) software revenue grew 63.1% in 2018 to $846 million. It became the fastest-growing segment of the global enterprise software market. It was slated to reach $1.3 billion in revenue by the end of 2019, a figure we have yet to check up on.
Even though RPA today is invading almost every industry, the major adopters of this tech are banks, insurance companies, telecom firms and utility companies. This is because companies in these sectors usually have legacy systems and RPA solutions get easily integrated with their existing functionalities.
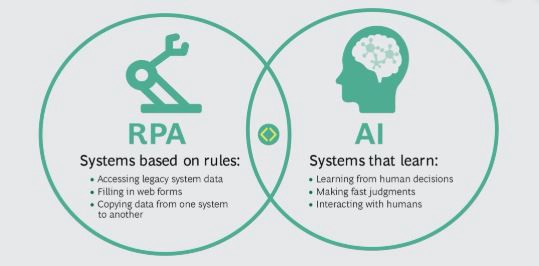
RPA is often mentioned in the same breath as artificial intelligence, deep learning, machine learning and natural language processing. However, there are differences — many people think every aspect of automation is artificial intelligence, which is not true. RPA and AI are two horizontal technologies with a different set of goals and interfaces.
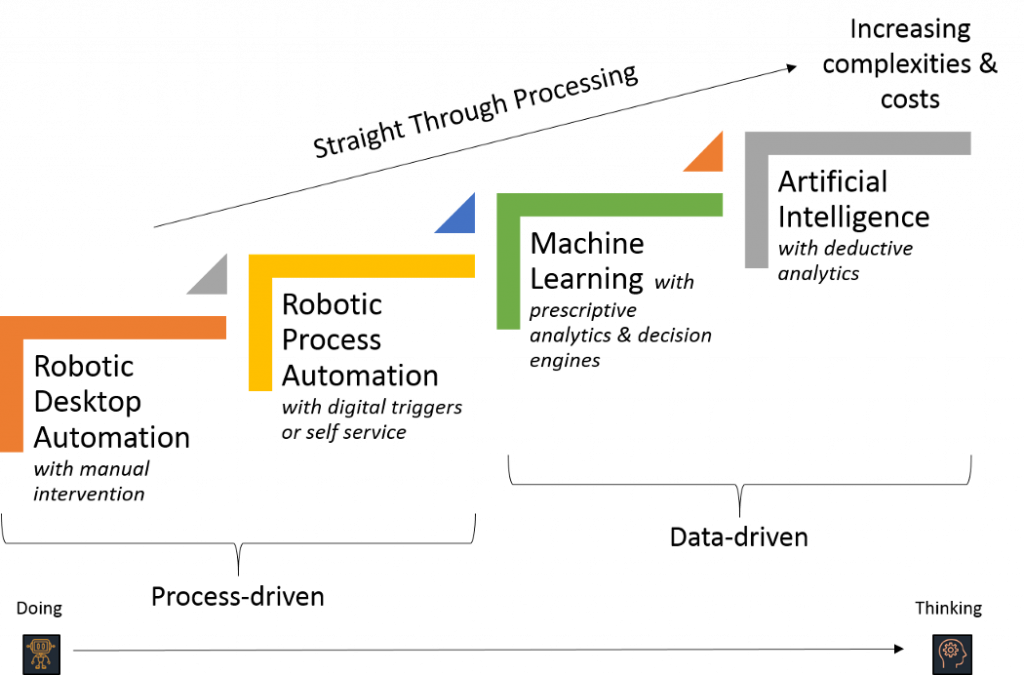
It’s easy to get robotic process automation (RPA), machine learning (ML), and artificial intelligence (AI) mixed up—especially when people use them interchangeably. It can be confusing to differentiate between the three when they’re flying around in conversation, but they’re not as mystical as they seem: You use them every day when you ask Alexa to set a timer, listen to your recommended songs on Spotify, or break down and order those footie pajamas that Amazon has been recommending you to buy for the last two weeks (just me, or…?).

What is RPA?
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a software that helps a human automate a manual process. Unlike ML and AI, which are data-driven, RPA is process-driven. By process-driven, I mean that RPA works by being given pre-built processes—ones that are repetitive, rule-based, and usually require the human end-user to interact with more than one line-of-business system (such as SharePoint and Office 365)—that it then automates for the human end-user. Think of it as RPA being the brawn and ML and AI being the brains.
The Real Difference Between RPA & AI
AI is basically about a computer’s ability to mimic human mentality — whether it’s about recognising an image or even solving a problem or a debate.
You can take a look at Facebook’s AI Research to understand better. Here, the social media giant feeds the AI system with different images and the machine delivers exacts results. When a photo of a dog is shown to the machine, it not only recognised it as a dog but also recognised the breed.
RPA is a technology that uses a specific set of rules and an algorithm and based on that it automates a task. While AI is focused more on doing a human-level task, RPA is practically a software that reduces human efforts — it is about saving the business and white-collar workers’ time. Some of the most common examples of RPA are transferring data from one system to another, payroll processing, forms processing etc.
Even though AI is steps ahead than RPA, these two techs have the capability to take things to the next level if both are combined. For example, suppose you need your documents to be in a specific format to get them scanned, and RPA does this job. If you use an AI system that would filter out the poorly formatted or unsuitable documents, the work of the RPA would be much easier. And this collaboration is called Automation Continuum.
What is Machine Learning (ML) and What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?


Finally, we’ve reached the most mystified, easily misunderstood of the three terms.
Although artificial intelligence can seem like magic, behind the scenes, there’s really nothing mystical about it. At a high level, AI is essentially an umbrella term for various software—such as machine learning, as I mentioned earlier—that can demonstrate intelligence. Unlike RPA, AI is driven by data. And while machine learning aims to acquire knowledge, AI actually aims to become more intelligent. Its goal is to simulate intelligence. Most recently, AI’s been in the news for its use in creating FaceApp, the app that uses AI technology to produce a creepily realistic aged version of a photo of your face. But probably the most well-known example of AI today is Sophia, the human-like robot created by Hanson Robotics in 2016. Sophia can (for the most part) hold conversations and generally act like a real person (again, for the most part). She doesn’t have a scalp though.
The Future
The rate at which the RPA and AI are evolving, the market definitely looks brighter in the coming years. Even giant companies like IBM, Microsoft and SAP are tapping more and more to RPA. Meaning, they are increasing the awareness and traction of RPA software. Furthermore, new vendors are also emerging and a rapid pace and have started to be marking their presence in the industry.
However, it is not just RPA that is the talk of the talk, the role of AI is also one of the most significant things at present. The idea of Automation Continuum is becoming popular among a lot of organisations. The industry is now witnessing their capabilities and why not — AI can read, listen, and analyse and then feed data into bots that can create output, package it, and send it off. At the end of the day, RPA and AI are two valuable techs that organisations can use to aid their organisation’s digital transformation.
Looking into the future, it seems that more than talks about RPA and AI taking human jobs off, the talks about machine becoming humans’ sidekick will be more.

So what do you do when all signs point to having to go to University to gain any sort of advantage? Unfortunately it’s the current state of affairs that most employers will not hire you unless you have a degree for even junior or starting jobs. Once you have that degree, coming to my Mentor Program, with 1000ml with our Patent Pending training system, the only such system in the world; is the only way to gain the practical knowledge and experience that will jump start your career.
Check out our next dates below for our upcoming seminars, labs and programs, we’d love to have you there.
